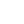We are happy to help you. Fill out our contact form, and we will get back to you immediately!
Exposure parameters: 100 kV – 8 mA – 17,9 s – 641 mGycm2, FOV: 4 x 4 cm
Clinical background and issue
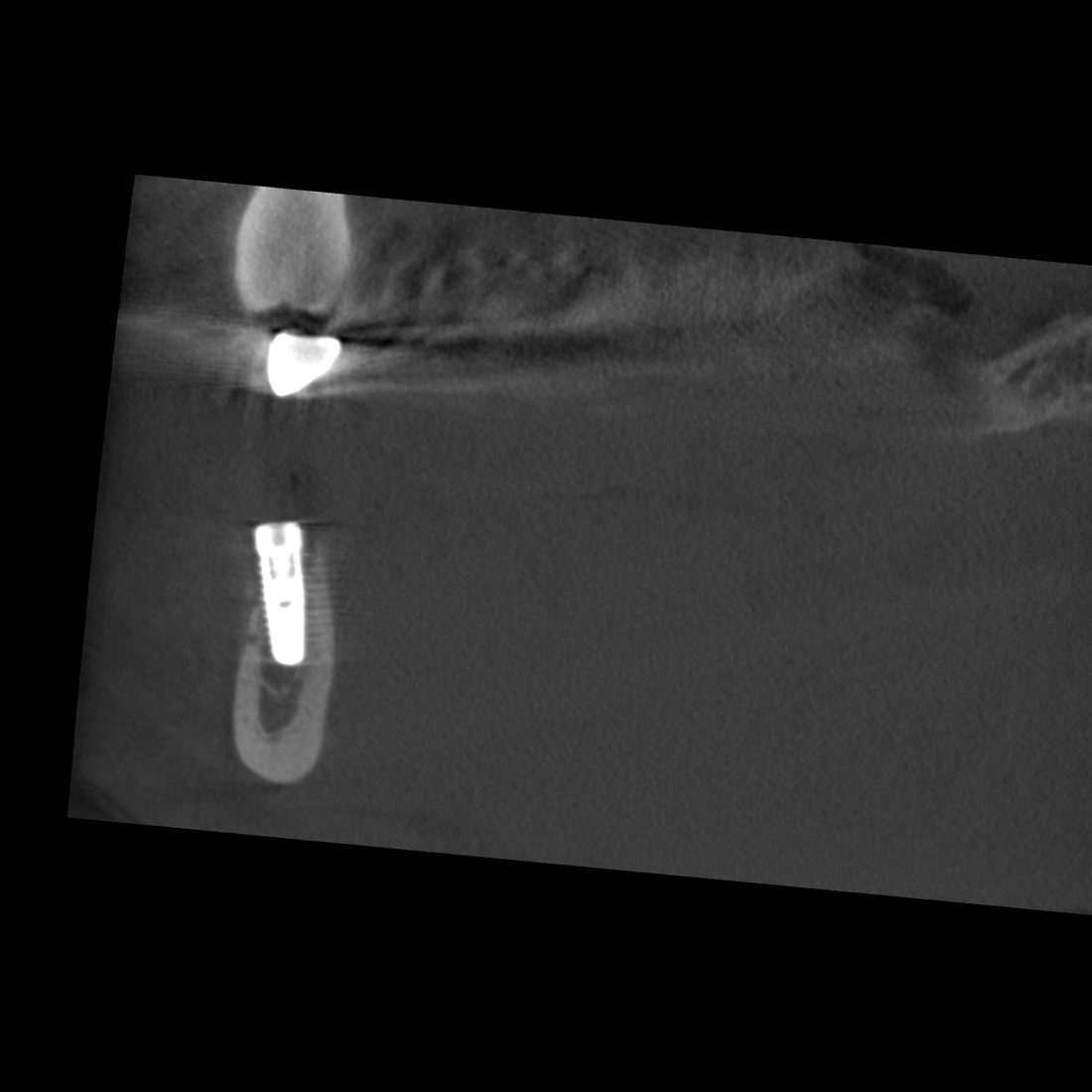
The layered panoramic image shows a hypodense cystic structure projected onto positions 43–45. Teeth 43 and 44 showed clinical vitality. The DVT study was acquired to clarify the spatial extent of the alteration, and the panoramic image shows a hypodense cystic structure projected onto the region 43-45. Teeth 43 and 44 showed clinical vitality. The DVT investigation was performed with a view to clarifying the spatial extent of the change.
Description
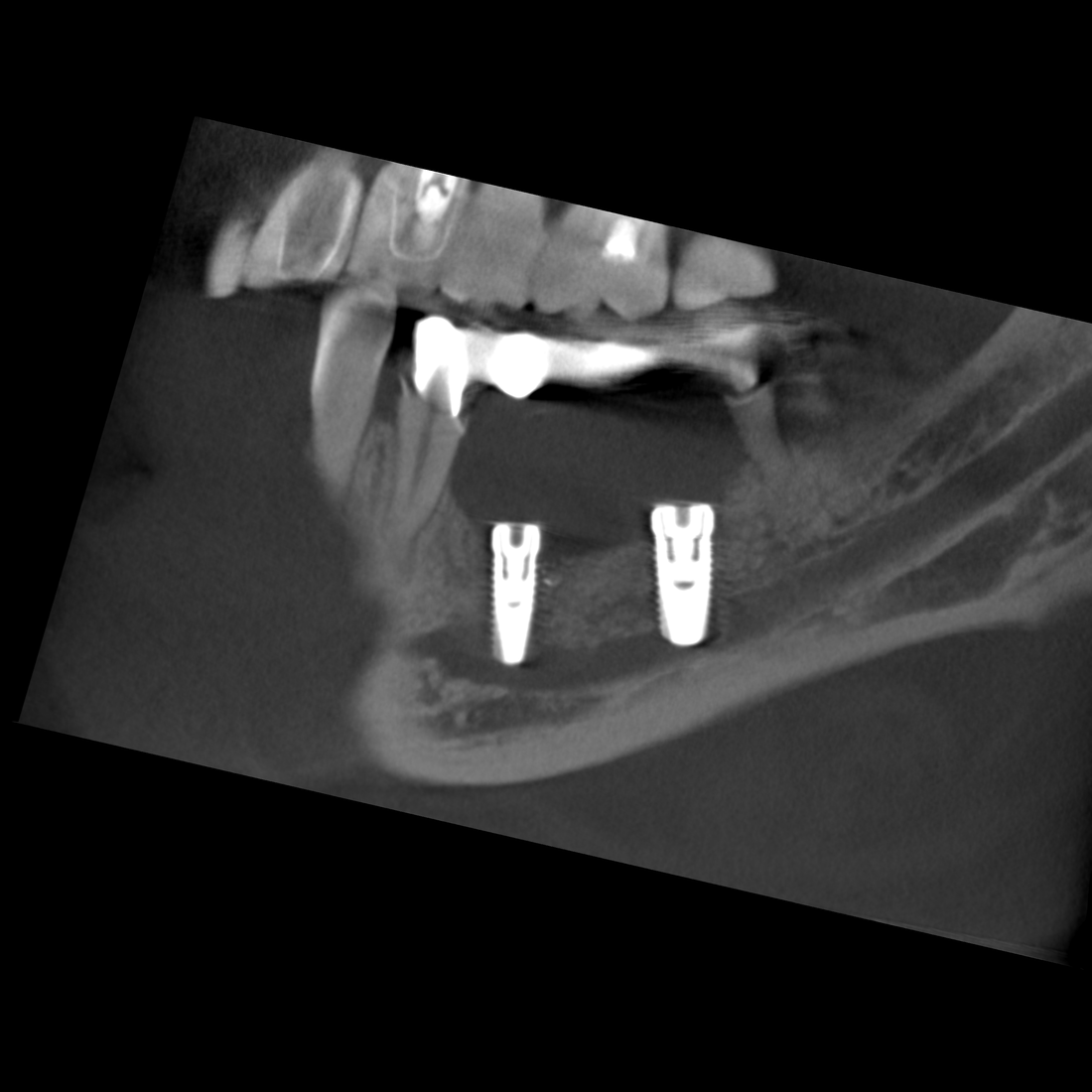
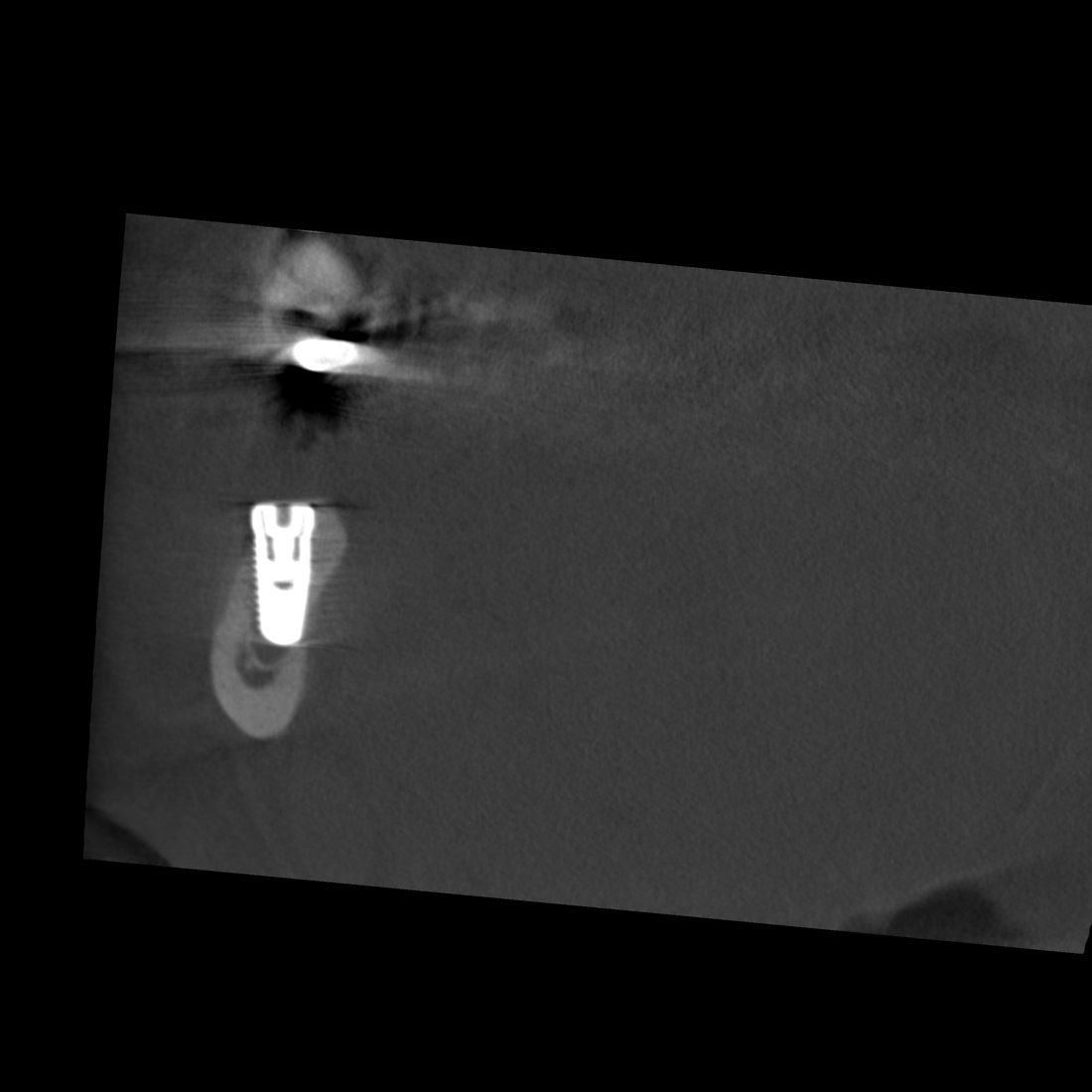
The space-occupying mass stretches in the caudal direction from the apices of teeth 43 and 44 as far as the basal compact bone and from the vestibular to the lingual compact bone, with the latter compact structures thinned out as a result of the space-occupying mass. The dorsal pole of the change is directly level with the branch of the right side of the mandibular canal that rises toward the mental foramen in a cranial and buccal direction. The parts of the mandibular incisive canal that lead toward the symphysis are crowded into the vestibular compact bone as a result of the space-occupying mass.
Findings
The position of this change at the transition between the osseous base and the alveolar process as well as the crowding out of adjacent anatomical structures are typical of a solitary bone cyst. The kind of aneurysmatic bone lesion most commonly cited from a differential diagnosis perspective does not result in any displacement of adjacent structures.